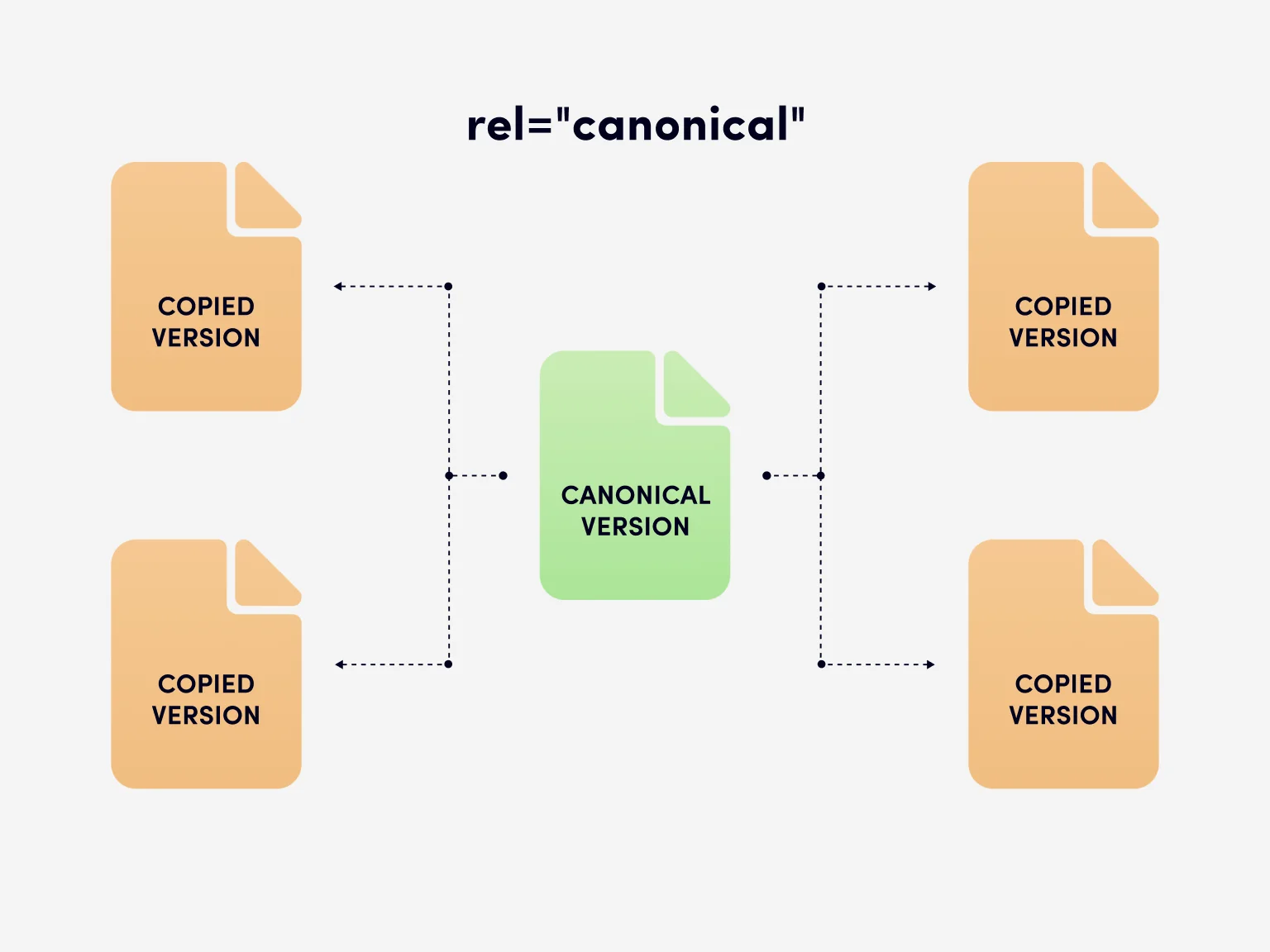
Canonical SEO refers to the process of indicating which version of a page search engines should treat as the primary or preferred one when multiple URLs contain similar or identical content. The definition of Canonical SEO centers on canonicalization signals that help search engines understand how different web pages relate to one another.
This practice reduces confusion during indexing and helps prevent duplicate content issues that can affect search results. In practical terms, canonical SEO guides search engines to a single, authoritative URL while allowing multiple URLs to coexist.
This explanation reflects how technical SEO documentation approaches the topic and aligns with how teams like SSinvent address canonicalization within advanced SEO services focused on site structure and indexing behavior.
Key Takeaways
- Canonical SEO is the practice of signaling the preferred version of a page to search engines when multiple URLs show the same or very similar content, helping consolidate indexing and ranking signals.
- A canonical URL in SEO does not remove other pages from the site; it signals to search engines to prioritize one primary page in search results, improving clarity and crawl efficiency.
- Google treats canonical tags as strong hints rather than strict rules, evaluating them alongside other signals such as internal links, redirects, and overall site structure.
- Canonical tags are most useful for managing duplicate pages created by URL parameters, product variations, HTTP versus HTTPS versions, or tracking URLs.
- Clear implementation using absolute URLs, consistent signals, and correct placement in HTML or CMS platforms helps prevent common canonical errors and improves search engine understanding.
What Does Canonical Mean in SEO?
In SEO, the word “canonical” means preferred or primary. When search engines crawl web pages, they may encounter multiple URLs that show the same or very similar content.
Canonicalization helps search engines decide which version of a page should be treated as the main reference in search results. Without clear signals, search engines may split ranking signals across several URLs.
Canonical in simple terms
In simple terms, a canonical URL tells search engines, “this is the page that matters most.” Other similar pages still exist, but the canonical version should appear in search results. This is especially useful for blog post archives, product pages, or pages with tracking parameters. The goal is clarity, not removal.
Is canonical the same as official?
Canonical does not always mean official in a legal or branding sense. In SEO, canonical refers to preference, not ownership or authority outside search engines. A preferred page can change based on technical signals, internal links, or content structure. Search engines treat canonical hints as guidance rather than strict commands.
What Is a Canonical URL in SEO?
A canonical URL in SEO is the URL that search engines consider the main version of a page. This URL consolidates signals from similar pages, such as links and relevance. Canonical URLs help search engines avoid indexing multiple URLs that show the same content. This improves clarity and supports efficient crawling.
Example of Canonical URL
A common example involves multiple URLs pointing to the same content, such as example.com/page and example.com/page?ref=tracking. Both URLs may return identical HTML, but only one should be the preferred page. By setting a canonical URL, the site signals which version of a page should be indexed. This process is known as canonicalization.
How Google Chooses the Canonical URL
Google canonical selection relies on multiple signals rather than a single tag. Search engines analyze internal links, external links, content similarity, and technical hints. The goal is to identify the page version that best represents the content. Canonicalization supports efficient use of crawl budget.
Google canonical signals
Google uses several signals to determine the preferred page. These include the internal linking structure, sitemap URLs, and rel=canonical tags. HTTP status codes also matter, especially when a page is 301 redirected to another URL. Consistency across signals increases the chance that Google selects the intended canonical.
Google canonical link vs tag
A Google canonical link refers broadly to signals that point to pages, while the Google canonical tag is a specific html element. The tag is placed in the head of html documents to indicate preference. Other signals, such as redirects and internal links, can reinforce or weaken the tag. Google evaluates all signals together.
What happens when signals conflict
When canonical signals conflict, Google may ignore the declared preference. For example, if a canonical tag points to one URL but internal links point elsewhere, search engines may choose a different preferred page. Conflicts can also arise from incorrect absolute URLs, inconsistent use of HTTP header directives, or mistakes during a website migration, as explained in this guide on bad website migration SEO. Clear alignment reduces this risk.
What Is the Google Canonical Tag?
The Google canonical tag is an HTML element that specifies the preferred URL for a page. It is written as a rel= “canonical” link in the < head> section of HTML documents. This tag helps search engines understand relationships between similar pages. It does not block indexing but guides consolidation.
Canonical tag in SEO example
An example of a canonical tag in SEO looks like <link rel=”canonical” href=”https://example.com/page”>. This tag points to pages that should be treated as the primary version. It is commonly used on duplicate pages or filtered views. The tag points clearly to the preferred page.
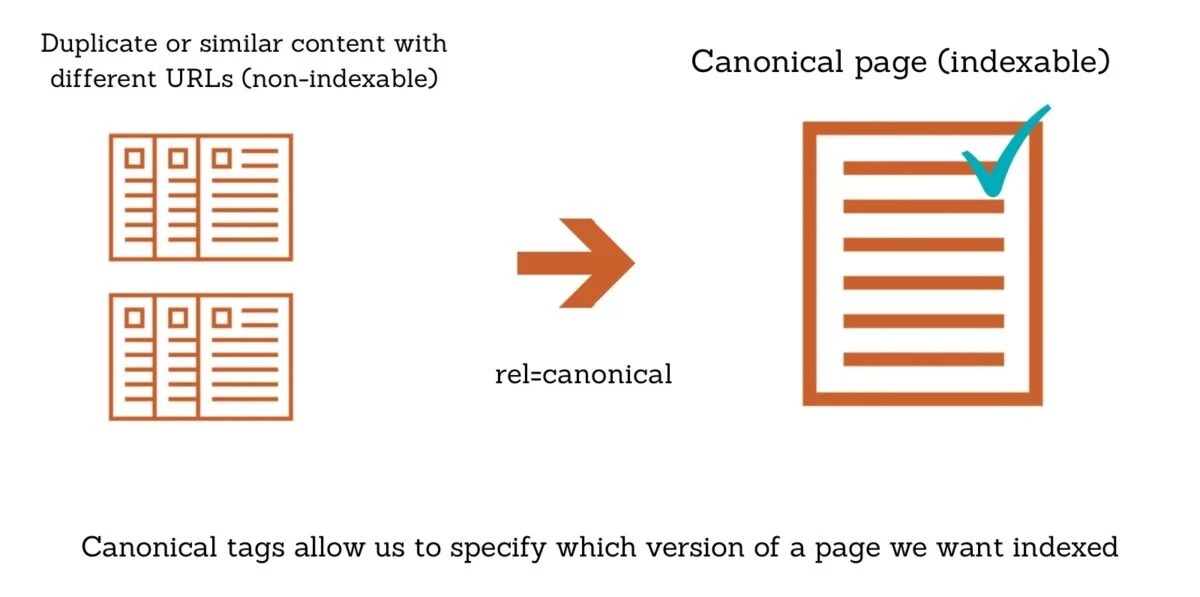
When to use a canonical tag
Canonical tags are useful when multiple URLs point to the same content. Common cases include product pages with sorting options or blog post URLs with tracking parameters. They are also helpful when content is syndicated across web pages. The key is that the content is similar, not entirely different.
How to Add a Canonical Tag
Adding a canonical tag requires placing the correct HTML element in the page head. The implementation must be accurate to avoid confusion. Both manual and CMS-based methods are common. The chosen approach depends on the site structure.
Adding canonical tags in HTML
To add a canonical tag in HTML, insert the rel canonical tag link into the head of the page. Use absolute URLs rather than relative ones to reduce ambiguity. Ensure the URL returns a valid status code and is not blocked. This method works for static html documents.
Adding canonical tags in WordPress
In WordPress, canonical tags are often handled by SEO plugins or the theme itself. These tools automatically generate canonical URLs based on page settings. Editors should verify that the generated canonical URL matches the intended preferred page. Manual overrides should be used with care.
Common Canonical Use Cases
Canonicalization applies to many everyday SEO scenarios. These cases often involve multiple URLs that serve similar pages. Proper use helps consolidate signals and improve indexing clarity. It also helps manage crawl budget.
Duplicate URLs
Duplicate pages often occur due to session IDs or tracking codes. Canonical tags help prevent duplicate content issues by signaling the main version of a page. This ensures that search engines do not treat duplicates as separate entries. Consolidation supports cleaner search results.
URL parameters
URL parameters can create many variations of the same page. Filters, sorting options, and pagination can all produce multiple URLs. Canonicalization helps search engines identify a preferred page. This is common for e-commerce product pages.
HTTP vs HTTPS
When both HTTP and HTTPS versions exist, canonical tags help indicate the secure version as the preferred page. This avoids confusion during indexing. It also supports consistent linking signals. Redirects and canonical tags often work together here.
Canonical Tag Best Practices
Canonical tags should always point to a valid, indexable page. Use absolute URLs and ensure consistency with internal links. Avoid chaining canonicals across many pages. Best practices emphasize clarity, simplicity, and signal alignment.
Common Canonical Errors
Common errors include pointing canonicals to non-indexable pages or blocked URLs. Using incorrect protocols or mismatched domains can also cause problems. Another issue is setting canonicals on pages that are not similar to other pages. These mistakes reduce effectiveness.
Canonical Tags vs Redirects and Noindex
Canonical tags differ from redirects and noindex directives. A canonical tag keeps multiple pages accessible while consolidating signals. A 301 redirect sends users and search engines to a different URL, which is why understanding scenarios such as a 301 redirect SEO penalty is important when choosing between redirects and canonical tags. Noindex removes a page from search results entirely. Each tool serves a different purpose.
Canonical Meaning Outside SEO
Outside of SEO, the word canonical has other meanings. These meanings can appear in unrelated search queries. Clarifying them helps avoid confusion for readers.
Canonical tag meaning in AO3
In fan communities like AO3, canonical refers to content that is officially part of a story’s universe. This meaning is unrelated to SEO or to the use of HTML elements. The overlap is linguistic, not technical. Context determines interpretation.
Canonicalization pronunciation
Canonicalization is pronounced “kuh-NAH-ni-kuh-lie-ZAY-shun.” The term refers to the process of selecting a preferred version. Understanding the pronunciation can help when discussing technical SEO topics verbally. The concept remains the same regardless of context.
This article explains canonicalization as a technical process that helps search engines manage similar pages, multiple urls, and indexing signals. By understanding how canonical tags, Google canonical signals, and preferred pages work together, readers can apply canonical SEO accurately and consistently.
Ready to see what SEO can do for your site?
If you want to understand where your site stands and what is holding back growth, schedule a call or request a free site audit. We will review your current visibility, technical setup, and content gaps, then outline clear next steps based on real data.